Fake and impersonation profiles have become a daily risk for individuals, brands, executives, and communities. Social platforms are more crowded than ever, and trust is often built in seconds based on a profile photo, username, or short bio. Unfortunately, this speed is exactly what scammers and impersonators exploit.
This guide explains how to detect fake profiles using profile consistency analysis. The methods described here apply to any social network and focus on practical verification rather than platform-specific tricks. If your goal is to verify a social media account or identify fake social media accounts before damage is done, this article will give you a clear and structured approach.
1. Why Fake Profiles Exist
Fake profiles are not created randomly. They exist because they work. As platforms grow and automation becomes cheaper, impersonation has evolved into a scalable business model.
According to the U.S. Federal Trade Commission, impersonation scams remain one of the most common and financially damaging forms of online fraud.
Popular Scams and Impersonation Scenarios
- Executive impersonation: Scammers copy the name and photo of a CEO or founder to contact employees, partners, or customers.
- Customer support fraud: Fake profiles pose as official brand support accounts and redirect users to phishing links.
- Romance and trust scams: Carefully crafted profiles build emotional trust before requesting money or personal data.
- Crypto and investment fraud: Impersonators pretend to be traders, analysts, or well known figures promising high returns.
- Reputation manipulation: Fake accounts are used to spread misinformation, fake reviews, or targeted harassment.
In most cases, the profile itself is the first and sometimes only line of defense. Learning how to detect fake profiles early is essential.
2. Signs of Impersonation: The Anatomy of a Bot
While fake profiles vary in quality, most of them share common patterns. These signals are easier to detect when you look at the account as a whole rather than focusing on one detail.
Generic or Empty Bios
Many fake accounts use vague descriptions like “Entrepreneur”, “Digital creator”, or “Crypto enthusiast” without context, location, or verifiable details. Real people usually mention specific roles, companies, or interests that can be cross-checked.
Stock Photos or Over-Perfect Faces
Profile images are often taken from stock libraries or generated using AI. Common signs include flawless skin, unnatural lighting, symmetrical facial features, and backgrounds that look staged rather than lived in.
Unbalanced Follower and Following Ratios
Fake accounts often follow hundreds or thousands of users while having very few followers. In other cases, bots inflate followers but show very low engagement, such as no comments or repetitive emoji replies.
A single red flag does not always mean a profile is fake. Multiple inconsistencies almost always do.
3. Cross-Platform Profile Consistency
One of the most effective ways to identify fake social media accounts is to check whether the identity exists consistently across platforms.
Role and Career Mismatch
If someone claims to be a CEO, founder, or public expert, they should usually have a presence on professional networks. For example, a profile stating “CEO of a global SaaS company” on Instagram that has no LinkedIn profile or company record is highly suspicious.
Username and Naming Patterns
Real users tend to reuse similar usernames across platforms. Impersonation profiles often use slight variations, added numbers, or extra characters because the original username is already taken.
Timeline Inconsistencies
Check posting history. If a person claims ten years of experience but their account was created recently and shows no historical content, the story does not align.
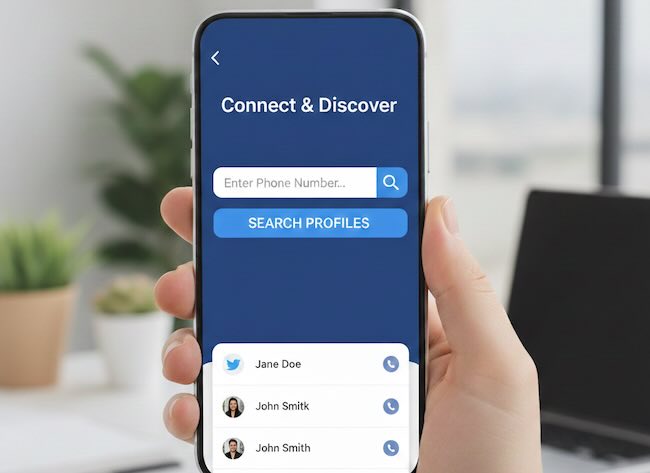
4. Using Username Search for Verification
Username search is one of the fastest ways to verify a social media account. By searching a username across multiple platforms, you can quickly identify whether an identity is established or artificially isolated.
What to Look For
- Presence on multiple networks with similar profile data
- Consistent profile photos and bios
- Mentions by other real users or websites
If a username exists only on one platform and appears nowhere else, especially for a supposedly public figure, caution is advised.
Dedicated tools like user search engines help automate this process and reveal hidden connections that manual checks often miss.
5. Reverse Image and Content Lookups
Reverse image search remains one of the strongest methods to detect fake profiles. It allows you to verify whether a profile photo is original or reused.
Detecting Stolen Photos
Upload the profile image to a reverse image search tool. If the same photo appears on unrelated websites, stock libraries, or under different names, the account is almost certainly fake.
Spotting AI-Generated Faces
AI-generated faces often have subtle flaws. Look closely at ears, glasses, teeth, and backgrounds. Blurred edges, asymmetry, or unnatural depth can indicate synthetic images.
Websites like This Person Does Not Exist demonstrate how realistic synthetic profile photos have become, making visual verification more important than ever.
Content Reuse Patterns
Fake accounts frequently recycle captions, posts, or comments. Copy a sentence from their posts and search it online. Identical content across multiple accounts is a strong signal of automation.
6. Date of Creation and Account History
The creation date of an account provides important context. New accounts are not automatically fake, but they are statistically more likely to be used in scams.
Why New Accounts Are Risky
- They have no long-term posting history
- They lack organic engagement
- They are often used for short-term fraud campaigns
If a new account immediately contacts users, promotes offers, or requests sensitive information, the risk increases significantly.
7. Public Indexing Limitations
Not all social media profiles are publicly indexed by search engines. Privacy settings, platform restrictions, and regional limitations can hide legitimate accounts from public search results.
This issue is explored in detail in Why You Cannot Find Some Profiles Online, which explains technical and privacy-related visibility limits.
This means absence from Google does not automatically indicate fraud. However, when combined with other red flags such as inconsistent data or reused images, lack of public presence becomes more meaningful.
8. Safety Recommendations
Verification is not only about detection but also about response. Once you suspect a fake profile, take protective steps immediately.
- Do not engage or share personal information
- Report the account to the platform
- Warn colleagues or followers if impersonation involves a real person or brand
- Document evidence such as screenshots and URLs
These verification principles are especially important on dating and marketplace platforms, where impersonation risks are higher. A focused guide is available in How to Verify Someone from Dating or Marketplace Apps.
For businesses and public figures, proactive monitoring is essential. Regular searches for names, usernames, and brand terms help detect impersonation early before it spreads.
9. Conclusion
Detecting fake or impersonation profiles is no longer optional. It is a core digital safety skill. By analyzing profile consistency, checking cross-platform presence, using reverse lookups, and understanding account history, you can verify social media accounts with far greater confidence.
No single signal proves deception. But when multiple inconsistencies align, the risk becomes clear. Awareness, verification, and proactive monitoring remain the strongest defense against impersonation.
10. Frequently Asked Questions
How can I detect a fake profile quickly?
Start by checking the profile photo, bio quality, follower engagement, and creation date. Then search the username across other platforms for consistency.
Are AI-generated profile photos common?
Yes. AI-generated faces are increasingly used because they avoid direct image theft. Look for unnatural details and run reverse image searches when possible.
Does a private profile mean it is fake?
No. Many real users keep their profiles private. Focus on consistency and behavior rather than privacy settings alone.
Why do impersonators copy executives and brands?
Trusted identities increase response rates. People are more likely to engage when they believe the profile represents authority or legitimacy.
What is the safest way to verify a social media account?
Use a combination of cross-platform checks, username search, and content verification. Relying on one method alone is not sufficient.